Ingrown Toenails
What is Onychocryptosis?
Onychocryptosis is the medical term used for ingrown toenails. Another less common term is Unguis incarnates. It is a common form of nail disease. While Onychocryptosis can occur on the nails of the hands, it most often affects the toenails. In this condition, the nails grow at an angle, which causes them to cut into the nail bed.
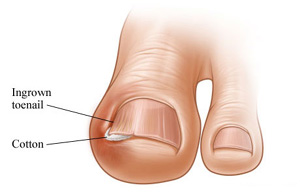
What are the symptoms of ingrown toenails?
The symptoms commonly include pain, swelling and redness along the outer edges and the base of the nail. The immune system reacts to the nail as a foreign invader and attempts to “wall off” the invader, which is actually the toenail. There may be pus or a bloody drainage. These are all signs of infection that may require professional treatment.
What causes ingrown toenails?
There are four primary causes. They are listed below, from most to least common.
- Bad maintenance—cutting the nails too short or rounding off the tips
- Shoes that are too tight, too narrow or too small in the toe-box—tight fitting socks or stockings, especially those that have seams that press on the toes
- Injury or trauma, such as a stubbed toe—running and other vigorous physical activity
- Nail deformities or diseases—genetic predisposition
How are ingrown toenails treated and prevented?
Prevention is easier than treatment, as it is with most things. You should wear comfortable shoes that are wide enough to accommodate your feet.
Learning how to cut your nails correctly, filing off the edges, if necessary is the second step. The use of toenail scissors, rather than clippers, can create an angle where the lower blade is either too far back or too far forward. Either way can contribute to ingrown toenails.
An extra-thin professional file will allow you to get lift and file, even in difficult to reach areas. Professional files can be purchased at FootSmart.com and other retailers.
To prevent infection, podiatrists recommend antiseptic sprays or lotions. They contain natural anti-bacterial and anti-fungal ingredients, including tea tree oil, camphor and menthol. They can be used to reduce pain and on a regular basis to prevent infection.
In serious cases, a podiatrist should be consulted for ingrown toenails. Bathroom surgery is not recommended.



This article is very informative. A Podiatrist can be consulted for advice even if you are not experiencing pain from your Ingrown Toenail. Nail Surgery is a permanent cure for an Ingrown Toenail and is quick and painless. COnsult your Podiatrist for further information.